Problem
Given an n x n array of integers matrix, return **the *minimum sum* of any falling path through** matrix.
A falling path starts at any element in the first row and chooses the element in the next row that is either directly below or diagonally left/right. Specifically, the next element from position (row, col) will be (row + 1, col - 1), (row + 1, col), or (row + 1, col + 1).
Example 1:
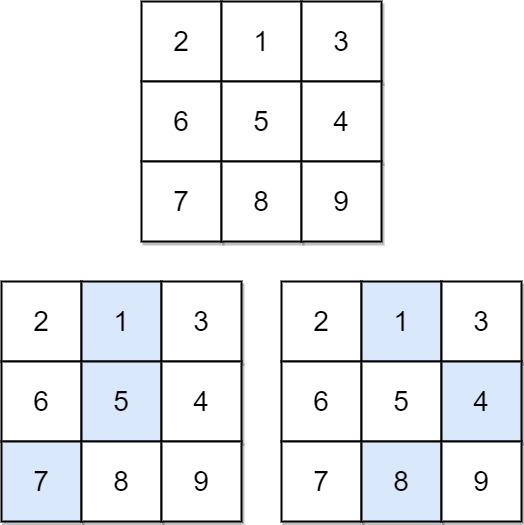
Input: matrix = [[2,1,3],[6,5,4],[7,8,9]]
Output: 13
Explanation: There are two falling paths with a minimum sum as shown.
Example 2:
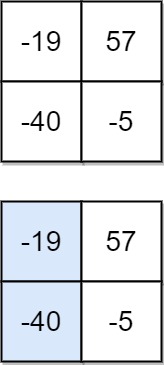
Input: matrix = [[-19,57],[-40,-5]]
Output: -59
Explanation: The falling path with a minimum sum is shown.
Constraints:
n == matrix.length == matrix[i].length1 <= n <= 100-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
Solution (Java)
class Solution {
public int minFallingPathSum(int[][] matrix) {
int l = matrix[0].length;
int[] arr = matrix[0];
for (int i = 1; i < matrix.length; i++) {
int[] cur = new int[l];
for (int j = 0; j < l; j++) {
int left = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int right = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int curCell = arr[j];
if (j > 0) {
left = arr[j - 1];
}
if (j < l - 1) {
right = arr[j + 1];
}
cur[j] = matrix[i][j] + Math.min(left, Math.min(right, curCell));
}
arr = cur;
}
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
if (arr[i] < min) {
min = arr[i];
}
}
return min;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).