Problem
You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array grid of size m x n that represents a map of the items in a shop. The integers in the grid represent the following:
0represents a wall that you cannot pass through.1represents an empty cell that you can freely move to and from.All other positive integers represent the price of an item in that cell. You may also freely move to and from these item cells.
It takes 1 step to travel between adjacent grid cells.
You are also given integer arrays pricing and start where pricing = [low, high] and start = [row, col] indicates that you start at the position (row, col) and are interested only in items with a price in the range of [low, high] (inclusive). You are further given an integer k.
You are interested in the positions of the k highest-ranked items whose prices are within the given price range. The rank is determined by the first of these criteria that is different:
Distance, defined as the length of the shortest path from the
start(shorter distance has a higher rank).Price (lower price has a higher rank, but it must be in the price range).
The row number (smaller row number has a higher rank).
The column number (smaller column number has a higher rank).
Return **the *k* highest-ranked items within the price range sorted by their rank (highest to lowest)**. If there are fewer than k reachable items within the price range, return *all of them*.
Example 1:
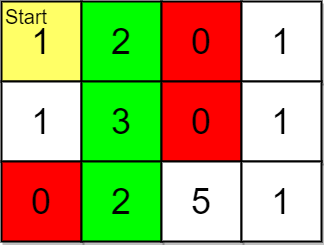
Input: grid = [[1,2,0,1],[1,3,0,1],[0,2,5,1]], pricing = [2,5], start = [0,0], k = 3
Output: [[0,1],[1,1],[2,1]]
Explanation: You start at (0,0).
With a price range of [2,5], we can take items from (0,1), (1,1), (2,1) and (2,2).
The ranks of these items are:
- (0,1) with distance 1
- (1,1) with distance 2
- (2,1) with distance 3
- (2,2) with distance 4
Thus, the 3 highest ranked items in the price range are (0,1), (1,1), and (2,1).
Example 2:
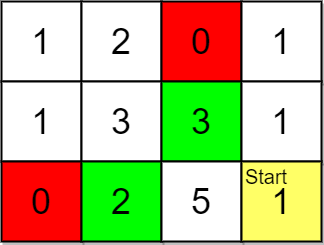
Input: grid = [[1,2,0,1],[1,3,3,1],[0,2,5,1]], pricing = [2,3], start = [2,3], k = 2
Output: [[2,1],[1,2]]
Explanation: You start at (2,3).
With a price range of [2,3], we can take items from (0,1), (1,1), (1,2) and (2,1).
The ranks of these items are:
- (2,1) with distance 2, price 2
- (1,2) with distance 2, price 3
- (1,1) with distance 3
- (0,1) with distance 4
Thus, the 2 highest ranked items in the price range are (2,1) and (1,2).
Example 3:
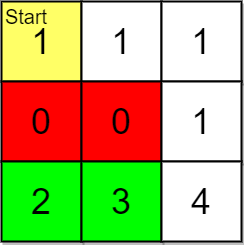
Input: grid = [[1,1,1],[0,0,1],[2,3,4]], pricing = [2,3], start = [0,0], k = 3
Output: [[2,1],[2,0]]
Explanation: You start at (0,0).
With a price range of [2,3], we can take items from (2,0) and (2,1).
The ranks of these items are:
- (2,1) with distance 5
- (2,0) with distance 6
Thus, the 2 highest ranked items in the price range are (2,1) and (2,0).
Note that k = 3 but there are only 2 reachable items within the price range.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10^51 <= m * n <= 10^50 <= grid[i][j] <= 10^5pricing.length == 22 <= low <= high <= 10^5start.length == 20 <= row <= m - 10 <= col <= n - 1grid[row][col] > 01 <= k <= m * n
Solution (Java)
class Solution {
static class Item {
int row;
int col;
int dist;
int price;
public Item(int row, int col, int dist, int price) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.dist = dist;
this.price = price;
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> highestRankedKItems(
int[][] grid, int[] pricing, int[] start, int k) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
Queue<int[]> bfs = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Item> items = new LinkedList<>();
bfs.add(start);
if (grid[start[0]][start[1]] >= pricing[0] && grid[start[0]][start[1]] <= pricing[1]) {
items.add(new Item(start[0], start[1], 0, grid[start[0]][start[1]]));
}
grid[start[0]][start[1]] = -1;
int distance = 0;
while (!bfs.isEmpty()) {
int size = bfs.size();
distance++;
while (size-- > 0) {
int[] loc = bfs.poll();
int[] dirX = {0, 1, -1, 0};
int[] dirY = {-1, 0, 0, 1};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = loc[0] + dirX[i];
int newY = loc[1] + dirY[i];
if (newX < 0
|| newX >= n
|| newY < 0
|| newY >= m
|| grid[newX][newY] == -1
|| grid[newX][newY] == 0) {
continue;
}
if (grid[newX][newY] >= pricing[0] && grid[newX][newY] <= pricing[1]) {
items.add(new Item(newX, newY, distance, grid[newX][newY]));
}
grid[newX][newY] = -1;
bfs.add(new int[] {newX, newY});
}
}
}
items.sort(
(a, b) -> {
int distDiff = a.dist - b.dist;
if (distDiff == 0) {
int priceDiff = a.price - b.price;
if (priceDiff == 0) {
int rowDiff = a.row - b.row;
if (rowDiff == 0) {
return a.col - b.col;
}
return rowDiff;
}
return priceDiff;
}
return distDiff;
});
List<List<Integer>> ans = new LinkedList<>();
while (k-- > 0 && !items.isEmpty()) {
Item item = items.poll();
ans.add(Arrays.asList(item.row, item.col));
}
return ans;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).