Problem
You are given an n x n binary grid board. In each move, you can swap any two rows with each other, or any two columns with each other.
Return **the minimum number of moves to transform the board into a *chessboard board***. If the task is impossible, return -1.
A chessboard board is a board where no 0's and no 1's are 4-directionally adjacent.
Example 1:
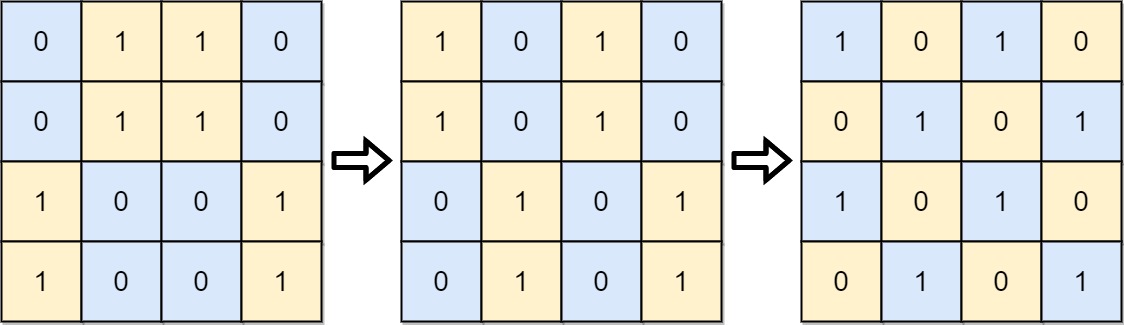
Input: board = [[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[1,0,0,1],[1,0,0,1]]
Output: 2
Explanation: One potential sequence of moves is shown.
The first move swaps the first and second column.
The second move swaps the second and third row.
Example 2:
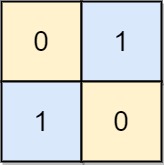
Input: board = [[0,1],[1,0]]
Output: 0
Explanation: Also note that the board with 0 in the top left corner, is also a valid chessboard.
Example 3:
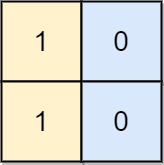
Input: board = [[1,0],[1,0]]
Output: -1
Explanation: No matter what sequence of moves you make, you cannot end with a valid chessboard.
Constraints:
n == board.lengthn == board[i].length2 <= n <= 30board[i][j]is either0or1.
Solution (Java)
class Solution {
public int movesToChessboard(int[][] board) {
int n = board.length;
int colToMove = 0;
int rowToMove = 0;
int rowOneCnt = 0;
int colOneCnt = 0;
for (int[] ints : board) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (((board[0][0] ^ ints[0]) ^ (ints[j] ^ board[0][j])) == 1) {
return -1;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
rowOneCnt += board[0][i];
colOneCnt += board[i][0];
if (board[i][0] == i % 2) {
rowToMove++;
}
if (board[0][i] == i % 2) {
colToMove++;
}
}
if (rowOneCnt < n / 2 || rowOneCnt > (n + 1) / 2) {
return -1;
}
if (colOneCnt < n / 2 || colOneCnt > (n + 1) / 2) {
return -1;
}
if (n % 2 == 1) {
// we cannot make it when ..ToMove is odd
if (colToMove % 2 == 1) {
colToMove = n - colToMove;
}
if (rowToMove % 2 == 1) {
rowToMove = n - rowToMove;
}
} else {
colToMove = Math.min(colToMove, n - colToMove);
rowToMove = Math.min(rowToMove, n - rowToMove);
}
return (colToMove + rowToMove) / 2;
}
}
Solution (C++)
class Solution {
public:
int movesToChessboard(vector<vector<int>>& b) {
int n = b.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(b[0][0] ^ b[0][j] ^ b[i][0] ^ b[i][j]) return -1;
}
}
int rowSum = 0;
int colSum = 0;
int rowSwap = 0;
int colSwap = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
rowSum += b[i][0];
colSum += b[0][i];
rowSwap += b[i][0] == i % 2;
colSwap += b[0][i] == i % 2;
}
if(rowSum != n/2 && rowSum != (n + 1)/2)return -1;
if(colSum != n/2 && colSum != (n + 1)/2)return -1;
if(n % 2 == 1){
if(colSwap % 2) colSwap = n - colSwap;
if(rowSwap % 2) rowSwap = n - rowSwap;
}else{
colSwap = min(colSwap, n - colSwap);
rowSwap = min(rowSwap, n - rowSwap);
}
return (rowSwap + colSwap)/2;
}
};
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).