Problem
You are given an integer array nums of 2 * n integers. You need to partition nums into two arrays of length n to minimize the absolute difference of the sums of the arrays. To partition nums, put each element of nums into one of the two arrays.
Return **the *minimum* possible absolute difference**.
Example 1:
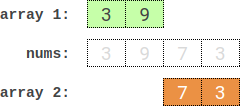
Input: nums = [3,9,7,3]
Output: 2
Explanation: One optimal partition is: [3,9] and [7,3].
The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((3 + 9) - (7 + 3)) = 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-36,36]
Output: 72
Explanation: One optimal partition is: [-36] and [36].
The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((-36) - (36)) = 72.
Example 3:
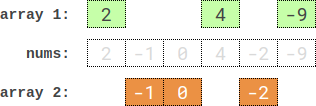
Input: nums = [2,-1,0,4,-2,-9]
Output: 0
Explanation: One optimal partition is: [2,4,-9] and [-1,0,-2].
The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((2 + 4 + -9) - (-1 + 0 + -2)) = 0.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 15nums.length == 2 * n-10^7 <= nums[i] <= 10^7
Solution
class Solution {
public int minimumDifference(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int n = nums.length / 2;
int sum = 0;
List<List<Integer>> arr1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> arr2 = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
arr1.add(new ArrayList<>());
arr2.add(new ArrayList<>());
if (i < n) {
sum += nums[i];
sum += nums[i + n];
}
}
for (int state = 0; state < (1 << n); state++) {
int sum1 = 0;
int sum2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if ((state & (1 << i)) == 0) {
continue;
}
int a1 = nums[i];
int a2 = nums[i + n];
sum1 += a1;
sum2 += a2;
}
int numOfEleInSet = Integer.bitCount(state);
arr1.get(numOfEleInSet).add(sum1);
arr2.get(numOfEleInSet).add(sum2);
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
Collections.sort(arr2.get(i));
}
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
List<Integer> sums1 = arr1.get(i);
List<Integer> sums2 = arr2.get(n - i);
for (int s1 : sums1) {
int idx = Collections.binarySearch(sums2, sum / 2 - s1);
if (idx < 0) {
idx = -(idx + 1);
}
if (idx < sums1.size()) {
min =
Math.min(
min,
Math.abs((sum - s1 - sums2.get(idx)) - (sums2.get(idx) + s1)));
}
if (idx - 1 >= 0) {
min =
Math.min(
min,
Math.abs(
(sum - s1 - sums2.get(idx - 1))
- (sums2.get(idx - 1) + s1)));
}
}
}
return min;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).