Problem
There is an undirected weighted connected graph. You are given a positive integer n which denotes that the graph has n nodes labeled from 1 to n, and an array edges where each edges[i] = [ui, vi, weighti] denotes that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi with weight equal to weighti.
A path from node start to node end is a sequence of nodes [z0, z1, z2, ..., zk] such that z0 = start and zk = end and there is an edge between zi and zi+1 where 0 <= i <= k-1.
The distance of a path is the sum of the weights on the edges of the path. Let distanceToLastNode(x) denote the shortest distance of a path between node n and node x. A restricted path is a path that also satisfies that distanceToLastNode(zi) > distanceToLastNode(zi+1) where 0 <= i <= k-1.
Return the number of restricted paths from node 1 to node n. Since that number may be too large, return it modulo 10^9 + 7.
Example 1:
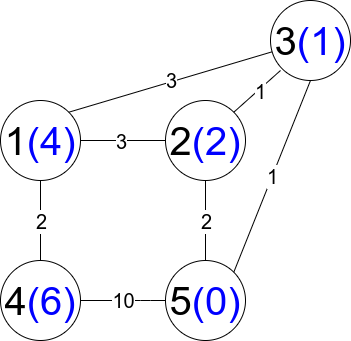
Input: n = 5, edges = [[1,2,3],[1,3,3],[2,3,1],[1,4,2],[5,2,2],[3,5,1],[5,4,10]]
Output: 3
Explanation: Each circle contains the node number in black and its distanceToLastNode value in blue. The three restricted paths are:
1) 1 --> 2 --> 5
2) 1 --> 2 --> 3 --> 5
3) 1 --> 3 --> 5
Example 2:
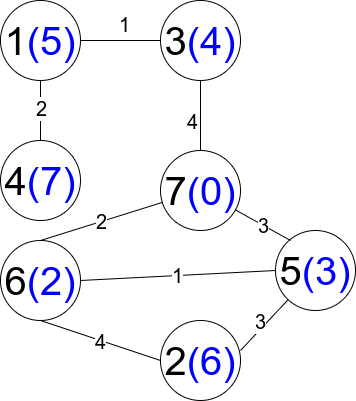
Input: n = 7, edges = [[1,3,1],[4,1,2],[7,3,4],[2,5,3],[5,6,1],[6,7,2],[7,5,3],[2,6,4]]
Output: 1
Explanation: Each circle contains the node number in black and its distanceToLastNode value in blue. The only restricted path is 1 --> 3 --> 7.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 2 * 10^4n - 1 <= edges.length <= 4 * 10^4edges[i].length == 31 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi1 <= weighti <= 10^5There is at most one edge between any two nodes.
There is at least one path between any two nodes.
Solution (Java)
class Solution {
private static class Pair implements Comparable<Pair> {
int v;
int cwt;
Pair(int v, int cwt) {
this.v = v;
this.cwt = cwt;
}
public int compareTo(Pair o) {
return this.cwt - o.cwt;
}
}
private static class Edge {
int v;
int wt;
Edge(int v, int wt) {
this.v = v;
this.wt = wt;
}
}
private int[] dtl;
private int[] dp;
private static final int M = 1000000007;
public int countRestrictedPaths(int n, int[][] edges) {
List<List<Edge>> graph = buildGraph(n, edges);
PriorityQueue<Pair> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n + 1];
dtl = new int[n + 1];
pq.add(new Pair(n, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Pair rem = pq.remove();
if (vis[rem.v]) {
continue;
}
dtl[rem.v] = rem.cwt;
vis[rem.v] = true;
for (Edge edge : graph.get(rem.v)) {
if (!vis[edge.v]) {
pq.add(new Pair(edge.v, rem.cwt + edge.wt));
}
}
}
dp = new int[n + 1];
return dfs(graph, 1, new boolean[n + 1], n);
}
private int dfs(List<List<Edge>> graph, int vtx, boolean[] vis, int n) {
if (vtx == n) {
return 1;
}
long ans = 0;
vis[vtx] = true;
for (Edge edge : graph.get(vtx)) {
if (!vis[edge.v] && dtl[edge.v] < dtl[vtx]) {
int x = dfs(graph, edge.v, vis, n);
ans = (ans + x) % M;
} else if (dtl[edge.v] < dtl[vtx] && vis[edge.v]) {
ans = (ans + dp[edge.v]) % M;
}
}
dp[vtx] = (int) ans;
return (int) ans;
}
private List<List<Edge>> buildGraph(int n, int[][] edges) {
List<List<Edge>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
int wt = edge[2];
graph.get(u).add(new Edge(v, wt));
graph.get(v).add(new Edge(u, wt));
}
return graph;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).