Problem
You are given a 0-indexed m x n integer matrix grid. Your initial position is at the top-left cell (0, 0).
Starting from the cell (i, j), you can move to one of the following cells:
- Cells
(i, k)withj < k <= grid[i][j] + j(rightward movement), or - Cells
(k, j)withi < k <= grid[i][j] + i(downward movement).
Return **the minimum number of cells you need to visit to reach the *bottom-right* cell** (m - 1, n - 1). If there is no valid path, return -1.
Example 1:
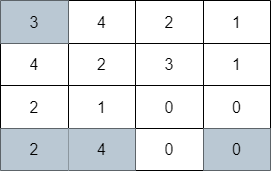
Input: grid = [[3,4,2,1],[4,2,3,1],[2,1,0,0],[2,4,0,0]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The image above shows one of the paths that visits exactly 4 cells.
Example 2:
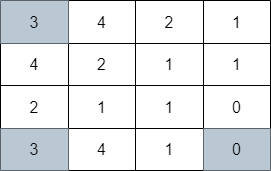
Input: grid = [[3,4,2,1],[4,2,1,1],[2,1,1,0],[3,4,1,0]]
Output: 3
Explanation: The image above shows one of the paths that visits exactly 3 cells.
Example 3:
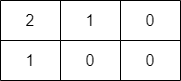
Input: grid = [[2,1,0],[1,0,0]]
Output: -1
Explanation: It can be proven that no path exists.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1051 <= m * n <= 1050 <= grid[i][j] < m * ngrid[m - 1][n - 1] == 0
Solution (Java)
class Solution {
public int minimumVisitedCells(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
int[] horizontals = new int[m], verticals = new int[n];
LinkedList<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new int[] {0, 0});
horizontals[0] = 1;
verticals[0] = 1;
for (int output = 1; !queue.isEmpty(); output++) for (int i = queue.size(); i > 0; i--) {
int[] t = queue.removeFirst();
int x = t[0], y = t[1];
if (x == m - 1 && y == n - 1) return output;
for (int j = Math.max(horizontals[x], y + 1); j <= grid[x][y] + y && j < n; j++) if (!visited[x][j]) {
visited[x][j] = true;
queue.add(new int[] {x, j});
}
while (horizontals[x] < n && visited[x][horizontals[x]]) horizontals[x]++;
for (int j = Math.max(verticals[y], x + 1); j <= grid[x][y] + x && j < m; j++) if (!visited[j][y]) {
visited[j][y] = true;
queue.add(new int[] {j, y});
}
while (verticals[y] < m && visited[verticals[y]][y]) verticals[y]++;
}
return -1;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).