Problem
Given a m x n binary matrix mat. In one step, you can choose one cell and flip it and all the four neighbors of it if they exist (Flip is changing 1 to 0 and 0 to 1). A pair of cells are called neighbors if they share one edge.
Return the minimum number of steps required to convert mat to a zero matrix or -1 if you cannot.
A binary matrix is a matrix with all cells equal to 0 or 1 only.
A zero matrix is a matrix with all cells equal to 0.
Example 1:
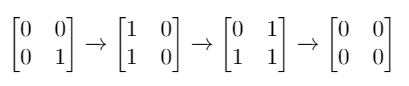
Input: mat = [[0,0],[0,1]]
Output: 3
Explanation: One possible solution is to flip (1, 0) then (0, 1) and finally (1, 1) as shown.
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[0]]
Output: 0
Explanation: Given matrix is a zero matrix. We do not need to change it.
Example 3:
Input: mat = [[1,0,0],[1,0,0]]
Output: -1
Explanation: Given matrix cannot be a zero matrix.
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 3mat[i][j]is either0or1.
Solution
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Set;
public class Solution {
private Set<Integer> visited;
private boolean isValid(int x, int y, int r, int c) {
return x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < r && y < c;
}
private List<Integer> next(Integer n, int r, int c) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int[] dx = {0, 0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0, 0};
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
Integer newMask = n;
for (int k = 0; k < dx.length; k++) {
int nx = i + dx[k];
int ny = j + dy[k];
if (isValid(nx, ny, r, c)) {
newMask = newMask ^ (1 << (nx * 3 + ny));
}
}
if (visited.add(newMask)) {
ans.add(newMask);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
public int minFlips(int[][] mat) {
int mask = 0;
int r = mat.length;
int c = mat[0].length;
if (r == 1 && c == 1) {
return mat[0][0] == 0 ? 0 : 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
mask |= (mat[i][j] << (i * 3 + j));
}
}
if (mask == 0) {
return 0;
}
visited = new HashSet<>();
Queue<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
int count = 1;
q.add(mask);
visited.add(mask);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int qSize = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < qSize; i++) {
Integer currMask = q.poll();
List<Integer> nextStates = next(currMask, r, c);
for (Integer nextState : nextStates) {
if (nextState == 0) {
return count;
}
q.add(nextState);
}
}
count++;
}
return -1;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).