Problem
Given a string s, find two disjoint palindromic subsequences of s such that the product of their lengths is maximized. The two subsequences are disjoint if they do not both pick a character at the same index.
Return **the *maximum* possible product of the lengths of the two palindromic subsequences**.
A subsequence is a string that can be derived from another string by deleting some or no characters without changing the order of the remaining characters. A string is palindromic if it reads the same forward and backward.
Example 1:
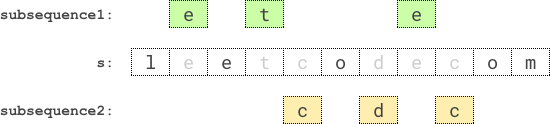
Input: s = "leetcodecom"
Output: 9
Explanation: An optimal solution is to choose "ete" for the 1st subsequence and "cdc" for the 2nd subsequence.
The product of their lengths is: 3 * 3 = 9.
Example 2:
Input: s = "bb"
Output: 1
Explanation: An optimal solution is to choose "b" (the first character) for the 1st subsequence and "b" (the second character) for the 2nd subsequence.
The product of their lengths is: 1 * 1 = 1.
Example 3:
Input: s = "accbcaxxcxx"
Output: 25
Explanation: An optimal solution is to choose "accca" for the 1st subsequence and "xxcxx" for the 2nd subsequence.
The product of their lengths is: 5 * 5 = 25.
Constraints:
2 <= s.length <= 12sconsists of lowercase English letters only.
Solution (Java)
class Solution {
public int maxProduct(String s) {
if (s.length() == 2) {
return 1;
}
List<State> list = new ArrayList<>();
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
Set<State> visited = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; ++i) {
int mask = 1 << i;
recur(chars, new State(i, i, 0, mask), list, visited);
recur(chars, new State(i, i + 1, 0, mask), list, visited);
}
list.sort((a, b) -> b.cnt - a.cnt);
int res = 1;
Set<Integer> explored = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size() - 1; ++i) {
if (explored.contains(i)) {
continue;
}
State cur = list.get(i);
if (cur.cnt == 1) {
break;
}
for (int j = i + 1; j < list.size(); ++j) {
State cand = list.get(j);
if ((cur.mask & cand.mask) < 1) {
if (explored.add(j)) {
res = Math.max(res, cur.cnt * cand.cnt);
}
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
private void recur(char[] chars, State s, List<State> list, Set<State> visited) {
if (s.i < 0 || s.j >= chars.length) {
return;
}
if (!visited.add(s)) {
return;
}
if (chars[s.i] == chars[s.j]) {
int m = s.mask | (1 << s.i) | (1 << s.j);
int nextCnt = s.cnt + (s.i < s.j ? 2 : 1);
list.add(new State(s.i, s.j, nextCnt, m));
recur(chars, new State(s.i - 1, s.j + 1, nextCnt, m), list, visited);
}
recur(chars, new State(s.i - 1, s.j, s.cnt, s.mask), list, visited);
recur(chars, new State(s.i, s.j + 1, s.cnt, s.mask), list, visited);
}
private static class State {
int i;
int j;
int cnt;
int mask;
public State(int i, int j, int cnt, int mask) {
this.i = i;
this.j = j;
this.cnt = cnt;
this.mask = mask;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == null || o.getClass() != this.getClass()) {
return false;
}
State s = (State) o;
return this.i == s.i && this.j == s.j && this.mask == s.mask;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (this.i * 31 + this.j) * 31 + this.mask;
}
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).