Problem
You are given an m x n integer matrix grid.
A rhombus sum is the sum of the elements that form the border of a regular rhombus shape in grid. The rhombus must have the shape of a square rotated 45 degrees with each of the corners centered in a grid cell. Below is an image of four valid rhombus shapes with the corresponding colored cells that should be included in each rhombus sum:
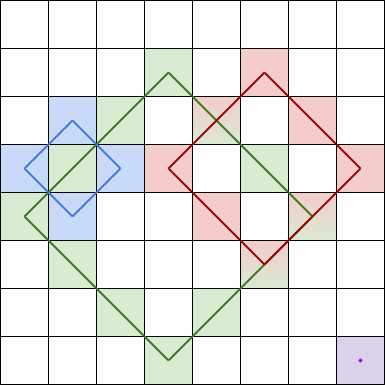
Note that the rhombus can have an area of 0, which is depicted by the purple rhombus in the bottom right corner.
Return **the biggest three *distinct rhombus sums* in the grid in descending order**. If there are less than three distinct values, return all of them.
Example 1:
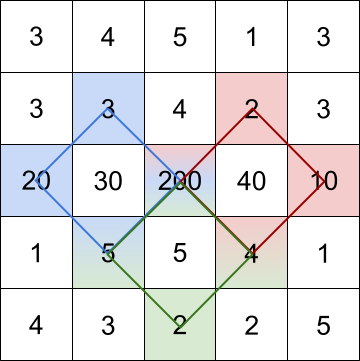
Input: grid = [[3,4,5,1,3],[3,3,4,2,3],[20,30,200,40,10],[1,5,5,4,1],[4,3,2,2,5]]
Output: [228,216,211]
Explanation: The rhombus shapes for the three biggest distinct rhombus sums are depicted above.
- Blue: 20 + 3 + 200 + 5 = 228
- Red: 200 + 2 + 10 + 4 = 216
- Green: 5 + 200 + 4 + 2 = 211
Example 2:
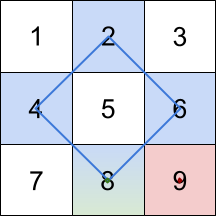
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [20,9,8]
Explanation: The rhombus shapes for the three biggest distinct rhombus sums are depicted above.
- Blue: 4 + 2 + 6 + 8 = 20
- Red: 9 (area 0 rhombus in the bottom right corner)
- Green: 8 (area 0 rhombus in the bottom middle)
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[7,7,7]]
Output: [7]
Explanation: All three possible rhombus sums are the same, so return [7].
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 501 <= grid[i][j] <= 10^5
Solution (Java)
class Solution {
public int[] getBiggestThree(int[][] grid) {
int capicity = 3;
PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[][][] preSum = new int[m][n][2];
int maxLen = Math.min(m, n) / 2;
for (int r = 0; r < m; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < n; c++) {
addToMinHeap(minHeap, grid[r][c], capicity);
preSum[r][c][0] +=
valid(m, n, r - 1, c - 1)
? grid[r][c] + preSum[r - 1][c - 1][0]
: grid[r][c];
preSum[r][c][1] +=
valid(m, n, r - 1, c + 1)
? grid[r][c] + preSum[r - 1][c + 1][1]
: grid[r][c];
}
}
for (int r = 0; r < m; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < n; c++) {
for (int l = 1; l <= maxLen; l++) {
if (!valid(m, n, r - l, c - l)
|| !valid(m, n, r - l, c + l)
|| !valid(m, n, r - 2 * l, c)) {
break;
}
int rhombus = preSum[r][c][0] - preSum[r - l][c - l][0];
rhombus += preSum[r][c][1] - preSum[r - l][c + l][1];
rhombus += preSum[r - l][c - l][1] - preSum[r - 2 * l][c][1];
rhombus += preSum[r - l][c + l][0] - preSum[r - 2 * l][c][0];
rhombus += -grid[r][c] + grid[r - 2 * l][c];
addToMinHeap(minHeap, rhombus, capicity);
}
}
}
int size = minHeap.size();
int[] res = new int[size];
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
res[i] = minHeap.poll();
}
return res;
}
private void addToMinHeap(PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap, int num, int capicity) {
if (minHeap.isEmpty() || (minHeap.size() < capicity && !minHeap.contains(num))) {
minHeap.offer(num);
} else {
if (num > minHeap.peek() && !minHeap.contains(num)) {
minHeap.poll();
minHeap.offer(num);
}
}
}
private boolean valid(int m, int n, int r, int c) {
return 0 <= r && r < m && 0 <= c && c < n;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).