Problem
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums, where nums[i] is a digit between 0 and 9 (inclusive).
The triangular sum of nums is the value of the only element present in nums after the following process terminates:
Let
numscomprise ofnelements. Ifn == 1, end the process. Otherwise, create a new 0-indexed integer arraynewNumsof lengthn - 1.For each index
i, where0 <= i < n - 1, assign the value ofnewNums[i]as(nums[i] + nums[i+1]) % 10, where%denotes modulo operator.Replace the array
numswithnewNums.Repeat the entire process starting from step 1.
Return the triangular sum of nums.
Example 1:
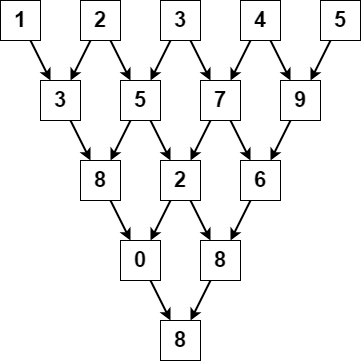
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 8
Explanation:
The above diagram depicts the process from which we obtain the triangular sum of the array.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5]
Output: 5
Explanation:
Since there is only one element in nums, the triangular sum is the value of that element itself.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10000 <= nums[i] <= 9
Solution (Java)
class Solution {
public int triangularSum(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
while (len-- > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
nums[i] += nums[i + 1];
nums[i] %= 10;
}
}
return nums[0];
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).