Problem
You are given a 0-indexed 1-dimensional (1D) integer array original, and two integers, m and n. You are tasked with creating a 2-dimensional (2D) array with m rows and n columns using all the elements from original.
The elements from indices 0 to n - 1 (inclusive) of original should form the first row of the constructed 2D array, the elements from indices n to 2 * n - 1 (inclusive) should form the second row of the constructed 2D array, and so on.
Return **an *m x n* 2D array constructed according to the above procedure, or an empty 2D array if it is impossible**.
Example 1:
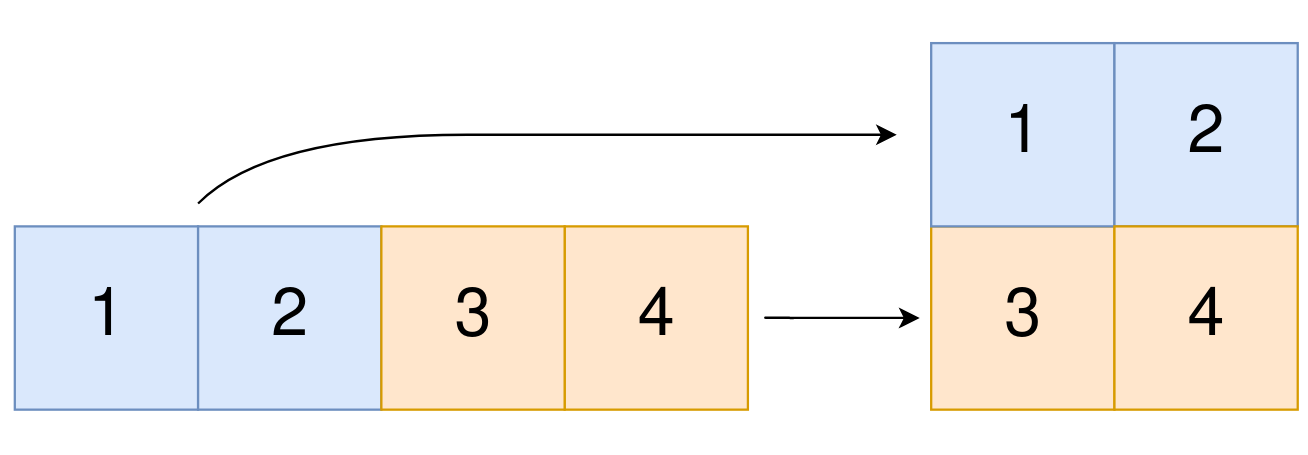
Input: original = [1,2,3,4], m = 2, n = 2
Output: [[1,2],[3,4]]
Explanation: The constructed 2D array should contain 2 rows and 2 columns.
The first group of n=2 elements in original, [1,2], becomes the first row in the constructed 2D array.
The second group of n=2 elements in original, [3,4], becomes the second row in the constructed 2D array.
Example 2:
Input: original = [1,2,3], m = 1, n = 3
Output: [[1,2,3]]
Explanation: The constructed 2D array should contain 1 row and 3 columns.
Put all three elements in original into the first row of the constructed 2D array.
Example 3:
Input: original = [1,2], m = 1, n = 1
Output: []
Explanation: There are 2 elements in original.
It is impossible to fit 2 elements in a 1x1 2D array, so return an empty 2D array.
Constraints:
1 <= original.length <= 5 * 10^41 <= original[i] <= 10^51 <= m, n <= 4 * 10^4
Solution (Java)
class Solution {
public int[][] construct2DArray(int[] original, int m, int n) {
int size = original.length;
if (m * n != size) {
return new int[][] {};
}
int[][] ans = new int[m][n];
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
ans[i][j] = original[k++];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).