Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, return the sum of all left leaves.
A leaf is a node with no children. A left leaf is a leaf that is the left child of another node.
Example 1:
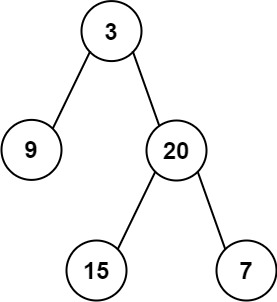
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 24
Explanation: There are two left leaves in the binary tree, with values 9 and 15 respectively.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: 0
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000].-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solution
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
traverse(root, arr);
return getSum(arr);
}
private void traverse(TreeNode root, List<Integer> arr) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null) {
arr.add(root.left.val);
}
traverse(root.left, arr);
traverse(root.right, arr);
}
private int getSum(List<Integer> arr) {
int sum = 0;
for (Integer integer : arr) {
sum += integer;
}
return sum;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).