Problem
You are given the head of a linked list.
The nodes in the linked list are sequentially assigned to non-empty groups whose lengths form the sequence of the natural numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, ...). The length of a group is the number of nodes assigned to it. In other words,
The
1stnode is assigned to the first group.The
2ndand the3rdnodes are assigned to the second group.The
4th,5th, and6thnodes are assigned to the third group, and so on.
Note that the length of the last group may be less than or equal to 1 + the length of the second to last group.
Reverse the nodes in each group with an even length, and return the head of the modified linked list.
Example 1:
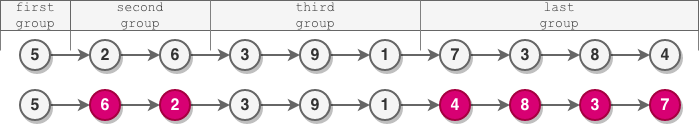
Input: head = [5,2,6,3,9,1,7,3,8,4]
Output: [5,6,2,3,9,1,4,8,3,7]
Explanation:
- The length of the first group is 1, which is odd, hence no reversal occurs.
- The length of the second group is 2, which is even, hence the nodes are reversed.
- The length of the third group is 3, which is odd, hence no reversal occurs.
- The length of the last group is 4, which is even, hence the nodes are reversed.
Example 2:
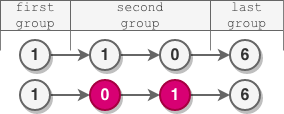
Input: head = [1,1,0,6]
Output: [1,0,1,6]
Explanation:
- The length of the first group is 1. No reversal occurs.
- The length of the second group is 2. The nodes are reversed.
- The length of the last group is 1. No reversal occurs.
Example 3:
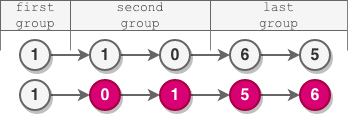
Input: head = [1,1,0,6,5]
Output: [1,0,1,5,6]
Explanation:
- The length of the first group is 1. No reversal occurs.
- The length of the second group is 2. The nodes are reversed.
- The length of the last group is 2. The nodes are reversed.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 10^5].0 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Solution (Java)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseEvenLengthGroups(ListNode head) {
int totalSize = size(head);
int curSize = 1;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (totalSize > 0) {
if (curSize % 2 == 0) {
ListNode[] arr = reverse(cur.next, curSize);
cur.next = arr[0];
arr[1].next = arr[2];
cur = arr[1];
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < curSize; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
totalSize -= curSize;
curSize = totalSize >= curSize + 1 ? curSize + 1 : totalSize;
}
return head;
}
private ListNode[] reverse(ListNode head, int size) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode forward;
ListNode cur = head;
while (size-- > 0) {
forward = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = forward;
}
ListNode[] arr = new ListNode[3];
arr[0] = prev;
arr[1] = head;
arr[2] = cur;
return arr;
}
private int size(ListNode head) {
int size = 0;
while (head != null) {
size++;
head = head.next;
}
return size;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).