Problem
Given the head of a singly linked list, group all the nodes with odd indices together followed by the nodes with even indices, and return the reordered list.
The first node is considered odd, and the second node is even, and so on.
Note that the relative order inside both the even and odd groups should remain as it was in the input.
You must solve the problem in O(1) extra space complexity and O(n) time complexity.
Example 1:
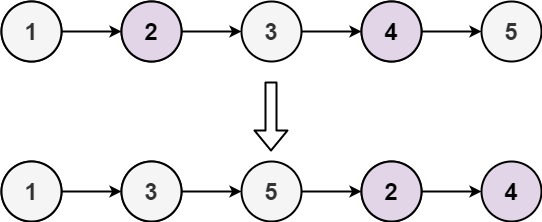
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [1,3,5,2,4]
Example 2:
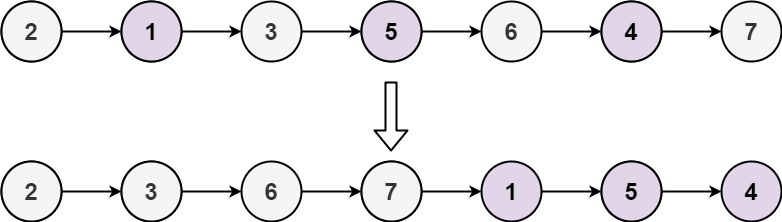
Input: head = [2,1,3,5,6,4,7]
Output: [2,3,6,7,1,5,4]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the linked list is in the range
[0, 10^4].-10^6 <= Node.val <= 10^6
Solution (Java)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if (head != null) {
ListNode odd = head;
ListNode even = head.next;
ListNode evenHead = even;
while (even != null && even.next != null) {
odd.next = odd.next.next;
even.next = even.next.next;
odd = odd.next;
even = even.next;
}
odd.next = evenHead;
}
return head;
}
}
Solution (Javascript)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var oddEvenList = function(head) {
// Handle base cases
if(!head || !head.next || !head.next.next) {
return head
}
// Set two pointers
let cur = head
let next = head.next
// Set the odd.next to point to the next even node
// Move each pointer up one node on each iteration
while(next && next.next) {
const temp = next.next
const temp2 = cur.next
cur.next = temp
next.next = temp.next
temp.next = temp2
cur = cur.next
next = next.next
}
return head
};
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).