Problem
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1 where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
At every node i, there is a gate. You are also given an array of even integers amount, where amount[i] represents:
the price needed to open the gate at node
i, ifamount[i]is negative, or,the cash reward obtained on opening the gate at node
i, otherwise.
The game goes on as follows:
Initially, Alice is at node
0and Bob is at nodebob.At every second, Alice and Bob each move to an adjacent node. Alice moves towards some leaf node, while Bob moves towards node
0. For every node along their path, Alice and Bob either spend money to open the gate at that node, or accept the reward. Note that:If the gate is already open, no price will be required, nor will there be any cash reward.
If Alice and Bob reach the node simultaneously, they share the price/reward for opening the gate there. In other words, if the price to open the gate is
c, then both Alice and Bob payc / 2each. Similarly, if the reward at the gate isc, both of them receivec / 2each.If Alice reaches a leaf node, she stops moving. Similarly, if Bob reaches node
0, he stops moving. Note that these events are independent of each other.
Return** the maximum net income Alice can have if she travels towards the optimal leaf node.**
Example 1:
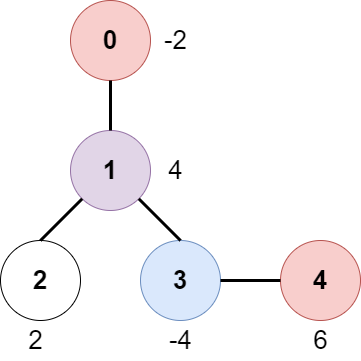
Input: edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[3,4]], bob = 3, amount = [-2,4,2,-4,6]
Output: 6
Explanation:
The above diagram represents the given tree. The game goes as follows:
- Alice is initially on node 0, Bob on node 3. They open the gates of their respective nodes.
Alice's net income is now -2.
- Both Alice and Bob move to node 1.
Since they reach here simultaneously, they open the gate together and share the reward.
Alice's net income becomes -2 + (4 / 2) = 0.
- Alice moves on to node 3. Since Bob already opened its gate, Alice's income remains unchanged.
Bob moves on to node 0, and stops moving.
- Alice moves on to node 4 and opens the gate there. Her net income becomes 0 + 6 = 6.
Now, neither Alice nor Bob can make any further moves, and the game ends.
It is not possible for Alice to get a higher net income.
Example 2:

Input: edges = [[0,1]], bob = 1, amount = [-7280,2350]
Output: -7280
Explanation:
Alice follows the path 0->1 whereas Bob follows the path 1->0.
Thus, Alice opens the gate at node 0 only. Hence, her net income is -7280.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != biedgesrepresents a valid tree.1 <= bob < namount.length == namount[i]is an even integer in the range[-104, 104].
Solution (Java)
class Solution {
int[] bobPath;
List<List<Integer>> tree;
boolean[] visited;
int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int[] amount;
//Finding a path that takes bob to node 0 and storing in bobPath array;
// -1 represents bob don't visit and values represents the level at which
// bob visits that place;
private boolean findBob(int n, int path){
if(n == 0){
bobPath[n] = path;
return true;
}
if(visited[n]) return false;
visited[n] = true;
bobPath[n] = path;
boolean isValid = false;
for(int i : tree.get(n)){
if(findBob(i, path+1)){
isValid = true;
break;
}
}
if(isValid) return true;
bobPath[n] = -1;
return false;
}
//Solving the alice profitable path based/
private void solve(int n, int alicePath, int aliceAns){
//If path already visitd by alice.
if(visited[n]) return;
//If alice and bob visits path at the same time.
if(bobPath[n] == alicePath)
aliceAns += (amount[n]/2);
//condition at which alice choose to open gate if bob didn't already.
else if(bobPath[n] == -1 || alicePath < bobPath[n])
aliceAns += amount[n];
//base case whenever alice reaches to the leaf node.
if(n != 0 && tree.get(n).size() == 1){
ans = Math.max(ans, aliceAns);
return;
}
visited[n] = true;
//Recursively alice trying to go to other leaf path.
for(int i : tree.get(n))
solve(i, alicePath+1, aliceAns);
}
public int mostProfitablePath(int[][] edges, int bob, int[] amount) {
int n = amount.length;
this.bobPath = new int[n];
this.amount = amount;
//Creating a tree.
tree = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tree.add(new ArrayList<>());
//Adding nodes to tree
for(int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++){
tree.get(edges[i][0]).add(edges[i][1]);
tree.get(edges[i][1]).add(edges[i][0]);
}
//Finding Bobs Path and storing on bobPath array
Arrays.fill(bobPath, -1);
visited = new boolean[n+1];
findBob(bob, 0);
//Solving fot alice.
visited = new boolean[n+1];
solve(0, 0, 0);
return ans;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).