Problem
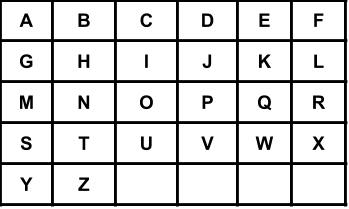
You have a keyboard layout as shown above in the X-Y plane, where each English uppercase letter is located at some coordinate.
- For example, the letter
'A'is located at coordinate(0, 0), the letter'B'is located at coordinate(0, 1), the letter'P'is located at coordinate(2, 3)and the letter'Z'is located at coordinate(4, 1).
Given the string word, return **the minimum total *distance* to type such string using only two fingers**.
The distance between coordinates (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is |x1 - x2| + |y1 - y2|.
Note that the initial positions of your two fingers are considered free so do not count towards your total distance, also your two fingers do not have to start at the first letter or the first two letters.
Example 1:
Input: word = "CAKE"
Output: 3
Explanation: Using two fingers, one optimal way to type "CAKE" is:
Finger 1 on letter 'C' -> cost = 0
Finger 1 on letter 'A' -> cost = Distance from letter 'C' to letter 'A' = 2
Finger 2 on letter 'K' -> cost = 0
Finger 2 on letter 'E' -> cost = Distance from letter 'K' to letter 'E' = 1
Total distance = 3
Example 2:
Input: word = "HAPPY"
Output: 6
Explanation: Using two fingers, one optimal way to type "HAPPY" is:
Finger 1 on letter 'H' -> cost = 0
Finger 1 on letter 'A' -> cost = Distance from letter 'H' to letter 'A' = 2
Finger 2 on letter 'P' -> cost = 0
Finger 2 on letter 'P' -> cost = Distance from letter 'P' to letter 'P' = 0
Finger 1 on letter 'Y' -> cost = Distance from letter 'A' to letter 'Y' = 4
Total distance = 6
Constraints:
2 <= word.length <= 300wordconsists of uppercase English letters.
Solution
class Solution {
private String word;
private Integer[][][] dp;
public int minimumDistance(String word) {
this.word = word;
dp = new Integer[27][27][word.length()];
return find(null, null, 0);
}
private int find(Character f1, Character f2, int index) {
if (index == word.length()) {
return 0;
}
Integer result = dp[f1 == null ? 0 : f1 - 'A' + 1][f2 == null ? 0 : f2 - 'A' + 1][index];
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
char ic = word.charAt(index);
int move = move(f1, ic) + find(ic, f2, index + 1);
move = Math.min(move, move(f2, ic) + find(f1, ic, index + 1));
dp[f1 == null ? 0 : f1 - 'A' + 1][f2 == null ? 0 : f2 - 'A' + 1][index] = move;
return move;
}
private int move(Character c1, Character c2) {
if (c1 == null) {
return 0;
}
int c1x = (c1 - 'A') % 6;
int c1y = (c1 - 'A') / 6;
int c2x = (c2 - 'A') % 6;
int c2y = (c2 - 'A') / 6;
return Math.abs(c1x - c2x) + Math.abs(c1y - c2y);
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).