Problem
Given an array arr of positive integers, consider all binary trees such that:
Each node has either
0or2children;The values of
arrcorrespond to the values of each leaf in an in-order traversal of the tree.The value of each non-leaf node is equal to the product of the largest leaf value in its left and right subtree, respectively.
Among all possible binary trees considered, return the smallest possible sum of the values of each non-leaf node. It is guaranteed this sum fits into a 32-bit integer.
A node is a leaf if and only if it has zero children.
Example 1:
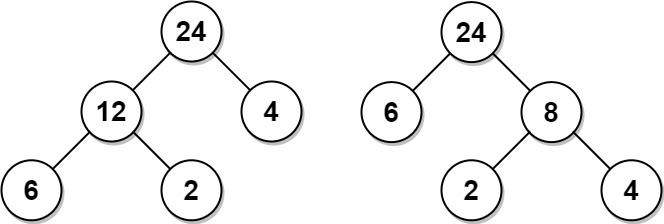
Input: arr = [6,2,4]
Output: 32
Explanation: There are two possible trees shown.
The first has a non-leaf node sum 36, and the second has non-leaf node sum 32.
Example 2:
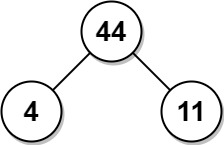
Input: arr = [4,11]
Output: 44
Constraints:
2 <= arr.length <= 401 <= arr[i] <= 15It is guaranteed that the answer fits into a 32-bit signed integer (i.e., it is less than 2^31).
Solution (Java)
class Solution {
public int mctFromLeafValues(int[] arr) {
int res = 0;
Deque<Integer> st = new ArrayDeque<>();
st.push(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
for (int num : arr) {
// do until the present num is bigger than nums in stack (we need to maintain the
// increasing order in stack (bottom to up))
while (st.peek() <= num) {
// find two smallest leafs (integer on top of stack is smallest and at bottom is
// largest UPTIL NOW)
// the next smaller leaf could either be present num or the
int smallestLeaf = st.pop();
int smallerLeaf = Math.min(st.peek(), num);
// num on top of stack after above pop()
// multiply minimum leafs to reduce the SUM
res += smallestLeaf * smallerLeaf;
}
st.push(num);
}
// if the size is 2 or less we do not to worry because we have already used it in above step
// since 1st num we added was Integer.MAX, and we do not need to use that, so just do this
// step if the size > 2 (basically there are at least 2 elements from the array)
while (st.size() > 2) {
int smallestLeaf = st.pop();
int smallerLeaf = st.peek();
res += smallestLeaf * smallerLeaf;
}
return res;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).