Problem
You are given a string s of length n, and an integer k. You are tasked to find the longest subsequence repeated k times in string s.
A subsequence is a string that can be derived from another string by deleting some or no characters without changing the order of the remaining characters.
A subsequence seq is repeated k times in the string s if seq * k is a subsequence of s, where seq * k represents a string constructed by concatenating seq k times.
- For example,
"bba"is repeated2times in the string"bababcba", because the string"bbabba", constructed by concatenating"bba"2times, is a subsequence of the string"**b**a**bab**c**ba**".
Return **the *longest subsequence repeated* k times in string s. If multiple such subsequences are found, return the lexicographically largest one. If there is no such subsequence, return an empty string**.
Example 1:
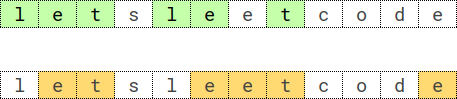
Input: s = "letsleetcode", k = 2
Output: "let"
Explanation: There are two longest subsequences repeated 2 times: "let" and "ete".
"let" is the lexicographically largest one.
Example 2:
Input: s = "bb", k = 2
Output: "b"
Explanation: The longest subsequence repeated 2 times is "b".
Example 3:
Input: s = "ab", k = 2
Output: ""
Explanation: There is no subsequence repeated 2 times. Empty string is returned.
Constraints:
n == s.length2 <= n, k <= 20002 <= n < k * 8sconsists of lowercase English letters.
Solution
class Solution {
public String longestSubsequenceRepeatedK(String s, int k) {
char[] ca = s.toCharArray();
char[] freq = new char[26];
for (char value : ca) {
++freq[value - 'a'];
}
ArrayList<String>[] cand = new ArrayList[8];
cand[1] = new ArrayList<>();
String ans = "";
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (freq[i] >= k) {
ans = "" + (char) ('a' + i);
cand[1].add(ans);
}
}
for (int i = 2; i < 8; i++) {
cand[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (String prev : cand[i - 1]) {
for (String c : cand[1]) {
String next = prev + c;
if (isSubsequenceRepeatedK(ca, next, k)) {
ans = next;
cand[i].add(ans);
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private boolean isSubsequenceRepeatedK(char[] ca, String t, int k) {
char[] ta = t.toCharArray();
int n = ca.length;
int m = ta.length;
int i = 0;
while (k-- > 0) {
int j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m) {
if (ca[i] == ta[j]) {
j++;
}
i++;
}
if (j != m) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).