Problem
You are given a tree with n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 in the form of a parent array parent where parent[i] is the parent of ith node. The root of the tree is node 0. Find the kth ancestor of a given node.
The kth ancestor of a tree node is the kth node in the path from that node to the root node.
Implement the TreeAncestor class:
TreeAncestor(int n, int[] parent)Initializes the object with the number of nodes in the tree and the parent array.int getKthAncestor(int node, int k)return thekthancestor of the given nodenode. If there is no such ancestor, return-1.
Example 1:
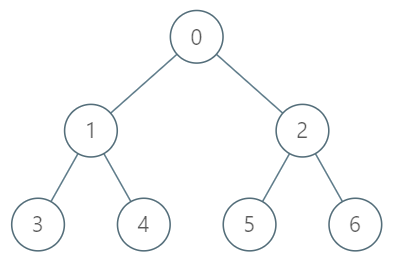
Input
["TreeAncestor", "getKthAncestor", "getKthAncestor", "getKthAncestor"]
[[7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]], [3, 1], [5, 2], [6, 3]]
Output
[null, 1, 0, -1]
Explanation
TreeAncestor treeAncestor = new TreeAncestor(7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]);
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(3, 1); // returns 1 which is the parent of 3
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(5, 2); // returns 0 which is the grandparent of 5
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(6, 3); // returns -1 because there is no such ancestor
Constraints:
1 <= k <= n <= 5 * 10^4parent.length == nparent[0] == -10 <= parent[i] < nfor all0 < i < n0 <= node < nThere will be at most
5 * 10^4queries.
Solution
class TreeAncestor {
private final List<Integer> steps;
private final Map<Integer, int[]> stepMap;
public TreeAncestor(int n, int[] parent) {
steps = new ArrayList<>();
stepMap = new HashMap<>();
steps.add(1);
stepMap.put(1, parent);
int stepBase = 10;
int step = stepBase;
while (step * 2 < n) {
int[] stepArr = new int[n];
int[] lastStepArr = stepMap.get(steps.get(steps.size() - 1));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int cur = i;
for (int repeat = 0; repeat < stepBase && cur != -1; repeat++) {
cur = lastStepArr[cur];
}
stepArr[i] = cur;
}
steps.add(step);
stepMap.put(step, stepArr);
step *= stepBase;
}
}
public int getKthAncestor(int node, int k) {
int index = steps.size() - 1;
while (k > 0 && node != -1 && index >= 0) {
int step = steps.get(index);
int[] stepArr = stepMap.get(step);
while (k >= step && node != -1) {
node = stepArr[node];
k -= step;
}
index--;
}
return node;
}
}
/**
* Your TreeAncestor object will be instantiated and called as such:
* TreeAncestor obj = new TreeAncestor(n, parent);
* int param_1 = obj.getKthAncestor(node,k);
*/
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).