Problem
You are given a stream of points on the X-Y plane. Design an algorithm that:
Adds new points from the stream into a data structure. Duplicate points are allowed and should be treated as different points.
Given a query point, counts the number of ways to choose three points from the data structure such that the three points and the query point form an axis-aligned square with positive area.
An axis-aligned square is a square whose edges are all the same length and are either parallel or perpendicular to the x-axis and y-axis.
Implement the DetectSquares class:
DetectSquares()Initializes the object with an empty data structure.void add(int[] point)Adds a new pointpoint = [x, y]to the data structure.int count(int[] point)Counts the number of ways to form axis-aligned squares with pointpoint = [x, y]as described above.
Example 1:
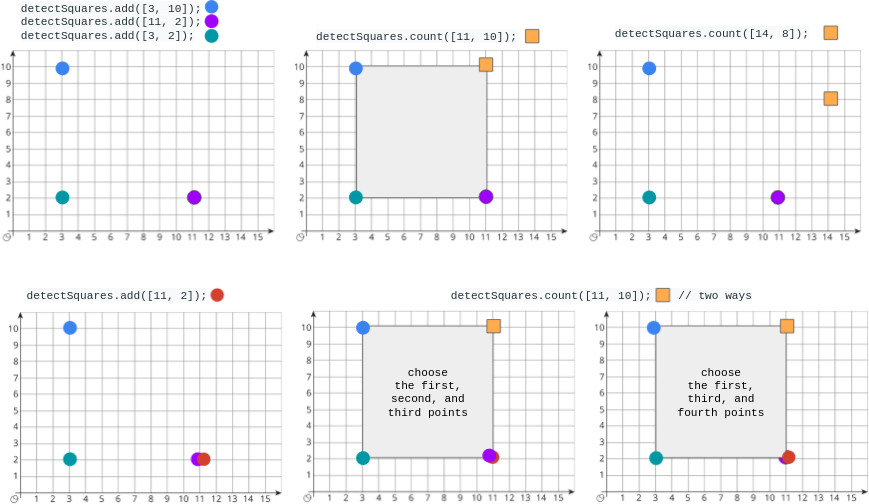
Input
["DetectSquares", "add", "add", "add", "count", "count", "add", "count"]
[[], [[3, 10]], [[11, 2]], [[3, 2]], [[11, 10]], [[14, 8]], [[11, 2]], [[11, 10]]]
Output
[null, null, null, null, 1, 0, null, 2]
Explanation
DetectSquares detectSquares = new DetectSquares();
detectSquares.add([3, 10]);
detectSquares.add([11, 2]);
detectSquares.add([3, 2]);
detectSquares.count([11, 10]); // return 1. You can choose:
// - The first, second, and third points
detectSquares.count([14, 8]); // return 0. The query point cannot form a square with any points in the data structure.
detectSquares.add([11, 2]); // Adding duplicate points is allowed.
detectSquares.count([11, 10]); // return 2. You can choose:
// - The first, second, and third points
// - The first, third, and fourth points
Constraints:
point.length == 20 <= x, y <= 1000At most
3000calls in total will be made toaddandcount.
Solution (Java)
class DetectSquares {
private static final int MUL = 1002;
private final Map<Integer, int[]> map;
public DetectSquares() {
this.map = new HashMap<>();
}
public void add(int[] point) {
int x = point[0];
int y = point[1];
int hash = x * MUL + y;
if (map.containsKey(hash)) {
map.get(hash)[2]++;
} else {
map.put(hash, new int[] {x, y, 1});
}
}
public int count(int[] point) {
int ans = 0;
int x = point[0];
int y = point[1];
for (Map.Entry<Integer, int[]> entry : map.entrySet()) {
int[] diap = entry.getValue();
int x1 = diap[0];
int y1 = diap[1];
int num = diap[2];
if (Math.abs(x - x1) == Math.abs(y - y1) && x != x1 && y != y1) {
int p1hash = x * MUL + y1;
int p2hash = x1 * MUL + y;
if (map.containsKey(p1hash) && map.containsKey(p2hash)) {
ans += map.get(p1hash)[2] * map.get(p2hash)[2] * num;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
/**
* Your DetectSquares object will be instantiated and called as such:
* DetectSquares obj = new DetectSquares();
* obj.add(point);
* int param_2 = obj.count(point);
*/
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).