Problem
Given a binary tree root and an integer target, delete all the leaf nodes with value target.
Note that once you delete a leaf node with value target**, **if its parent node becomes a leaf node and has the value target, it should also be deleted (you need to continue doing that until you cannot).
Example 1:
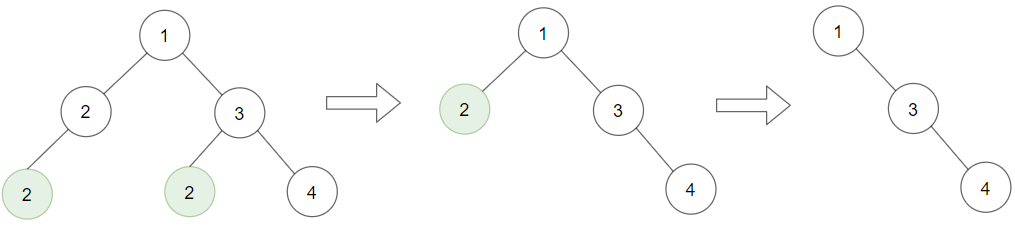
Input: root = [1,2,3,2,null,2,4], target = 2
Output: [1,null,3,null,4]
Explanation: Leaf nodes in green with value (target = 2) are removed (Picture in left).
After removing, new nodes become leaf nodes with value (target = 2) (Picture in center).
Example 2:
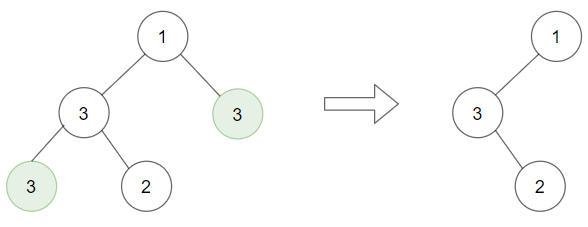
Input: root = [1,3,3,3,2], target = 3
Output: [1,3,null,null,2]
Example 3:
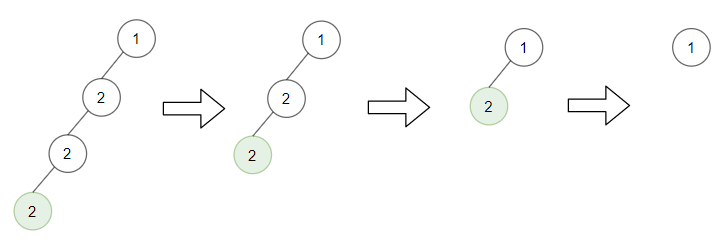
Input: root = [1,2,null,2,null,2], target = 2
Output: [1]
Explanation: Leaf nodes in green with value (target = 2) are removed at each step.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3000].1 <= Node.val, target <= 1000
Solution (Java)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode removeLeafNodes(TreeNode root, int target) {
while (hasTargetLeafNodes(root, target)) {
root = removeLeafNodes(target, root);
}
return root;
}
private TreeNode removeLeafNodes(int target, TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
if (root.val == target && root.left == null && root.right == null) {
root = null;
return root;
}
if (root.left != null
&& root.left.val == target
&& root.left.left == null
&& root.left.right == null) {
root.left = null;
}
if (root.right != null
&& root.right.val == target
&& root.right.left == null
&& root.right.right == null) {
root.right = null;
}
removeLeafNodes(target, root.left);
removeLeafNodes(target, root.right);
return root;
}
private boolean hasTargetLeafNodes(TreeNode root, int target) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && root.val == target) {
return true;
}
return hasTargetLeafNodes(root.left, target) || hasTargetLeafNodes(root.right, target);
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).