Problem
There are n servers numbered from 0 to n - 1 connected by undirected server-to-server connections forming a network where connections[i] = [ai, bi] represents a connection between servers ai and bi. Any server can reach other servers directly or indirectly through the network.
A critical connection is a connection that, if removed, will make some servers unable to reach some other server.
Return all critical connections in the network in any order.
Example 1:
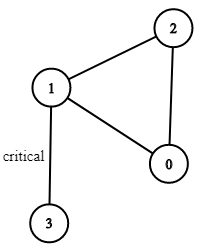
Input: n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[1,3]]
Output: [[1,3]]
Explanation: [[3,1]] is also accepted.
Example 2:
Input: n = 2, connections = [[0,1]]
Output: [[0,1]]
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 10^5n - 1 <= connections.length <= 10^50 <= ai, bi <= n - 1ai != biThere are no repeated connections.
Solution
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> criticalConnections(int n, List<List<Integer>> connections) {
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
// build graph
for (List<Integer> conn : connections) {
int x = conn.get(0);
int y = conn.get(1);
graph.get(x).add(y);
graph.get(y).add(x);
}
// record rank
int[] rank = new int[n];
// store result
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(graph, 0, 1, -1, rank, res);
return res;
}
// rank[] records the each node's smallest rank(min (it's natural rank, neighbors's smallest
// rank))
private int dfs(
List<List<Integer>> graph,
int node,
int time,
int parent,
int[] rank,
List<List<Integer>> res) {
if (rank[node] > 0) {
return rank[node];
}
// record the current natural rank for current node
rank[node] = time;
for (int nei : graph.get(node)) {
// skip the parent, since this is undirected graph
if (nei == parent) {
continue;
}
// step1 : run dfs to get the rank of this nei, if it is visited before, it will reach
// base case immediately
int neiTime = dfs(graph, nei, time + 1, node, rank, res);
// if neiTime is strictly larger than current node's rank, there is no cycle,
// connections between node and nei is a critically connection.
if (neiTime > time) {
res.add(Arrays.asList(nei, node));
}
// keep updating current node's rank with nei's smaller ranks
rank[node] = Math.min(rank[node], neiTime);
}
// return current node's rank to caller
return rank[node];
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).