Problem
Alice has an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. The tree is represented as a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1 where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Alice wants Bob to find the root of the tree. She allows Bob to make several guesses about her tree. In one guess, he does the following:
- Chooses two distinct integers
uandvsuch that there exists an edge[u, v]in the tree. - He tells Alice that
uis the parent ofvin the tree.
Bob's guesses are represented by a 2D integer array guesses where guesses[j] = [uj, vj] indicates Bob guessed uj to be the parent of vj.
Alice being lazy, does not reply to each of Bob's guesses, but just says that at least k of his guesses are true.
Given the 2D integer arrays edges, guesses and the integer k, return **the *number of possible nodes* that can be the root of Alice's tree**. If there is no such tree, return 0.
Example 1:
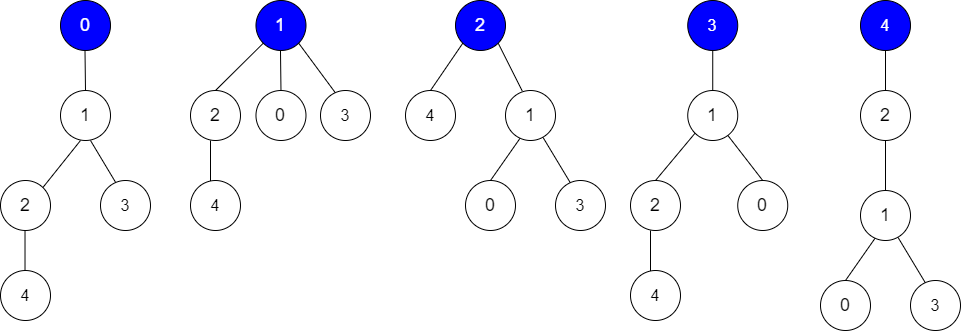
Input: edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[4,2]], guesses = [[1,3],[0,1],[1,0],[2,4]], k = 3
Output: 3
Explanation:
Root = 0, correct guesses = [1,3], [0,1], [2,4]
Root = 1, correct guesses = [1,3], [1,0], [2,4]
Root = 2, correct guesses = [1,3], [1,0], [2,4]
Root = 3, correct guesses = [1,0], [2,4]
Root = 4, correct guesses = [1,3], [1,0]
Considering 0, 1, or 2 as root node leads to 3 correct guesses.
Example 2:
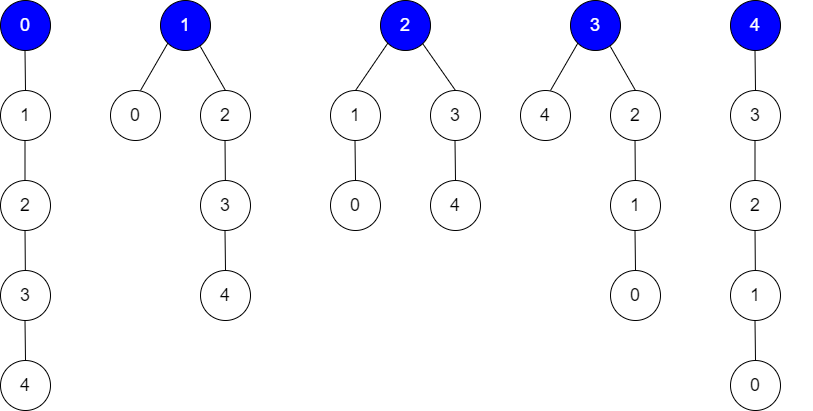
Input: edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4]], guesses = [[1,0],[3,4],[2,1],[3,2]], k = 1
Output: 5
Explanation:
Root = 0, correct guesses = [3,4]
Root = 1, correct guesses = [1,0], [3,4]
Root = 2, correct guesses = [1,0], [2,1], [3,4]
Root = 3, correct guesses = [1,0], [2,1], [3,2], [3,4]
Root = 4, correct guesses = [1,0], [2,1], [3,2]
Considering any node as root will give at least 1 correct guess.
Constraints:
edges.length == n - 12 <= n <= 1051 <= guesses.length <= 1050 <= ai, bi, uj, vj <= n - 1ai != biuj != vjedgesrepresents a valid tree.guesses[j]is an edge of the tree.guessesis unique.0 <= k <= guesses.length
Solution (Java)
class Solution {
public int rootCount(int[][] edges, int[][] guesses, int k) {
int n = edges.length + 1;
List<Integer>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];
Set<Integer>[] guessesGraph = new HashSet[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
guessesGraph[i] = new HashSet<>();
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
graph[edge[0]].add(edge[1]);
graph[edge[1]].add(edge[0]);
}
for (int[] guess : guesses) {
guessesGraph[guess[0]].add(guess[1]);
}
int res = 0;
Map<Long, Integer> memo = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i<n; i++) {
if (dfs(graph, guessesGraph, memo, i, -1) >= k) {
res++;
}
}
return res;
}
int dfs(List<Integer>[] graph, Set<Integer>[] guessesGraph, Map<Long, Integer> memo, int current, int prev) {
long key = (long)current * 1000000 + prev;
if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key);
int count = prev != -1 && guessesGraph[prev].contains(current) ? 1 : 0;
for (int next : graph[current]) {
if (next != prev) {
count += dfs(graph, guessesGraph, memo, next, current);
}
}
memo.put(key, count);
return count;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).