Problem
Given a binary tree root, a node X in the tree is named good if in the path from root to X there are no nodes with a value greater than X.
Return the number of good nodes in the binary tree.
Example 1:
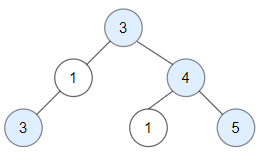
Input: root = [3,1,4,3,null,1,5]
Output: 4
Explanation: Nodes in blue are good.
Root Node (3) is always a good node.
Node 4 -> (3,4) is the maximum value in the path starting from the root.
Node 5 -> (3,4,5) is the maximum value in the path
Node 3 -> (3,1,3) is the maximum value in the path.
Example 2:
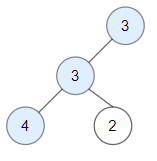
Input: root = [3,3,null,4,2]
Output: 3
Explanation: Node 2 -> (3, 3, 2) is not good, because "3" is higher than it.
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: 1
Explanation: Root is considered as good.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the binary tree is in the range
[1, 10^5].Each node's value is between
[-10^4, 10^4].
Solution
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int count = 0;
private void traverse(TreeNode root, int max) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.val >= max) {
count += 1;
max = root.val;
}
traverse(root.left, max);
traverse(root.right, max);
}
public int goodNodes(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
return count;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).