Problem
Given an array of integers preorder, which represents the preorder traversal of a BST (i.e., binary search tree), construct the tree and return its root.
It is guaranteed that there is always possible to find a binary search tree with the given requirements for the given test cases.
A binary search tree is a binary tree where for every node, any descendant of Node.left has a value strictly less than Node.val, and any descendant of Node.right has a value strictly greater than Node.val.
A preorder traversal of a binary tree displays the value of the node first, then traverses Node.left, then traverses Node.right.
Example 1:
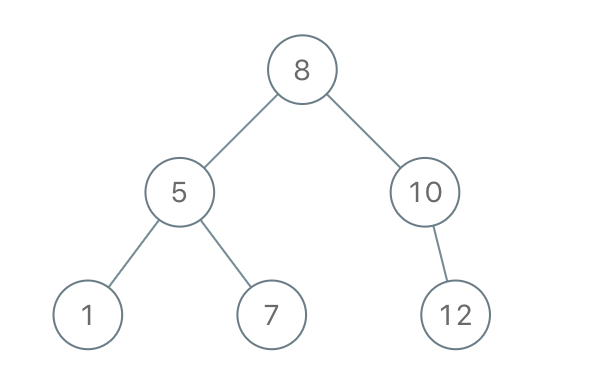
Input: preorder = [8,5,1,7,10,12]
Output: [8,5,10,1,7,null,12]
Example 2:
Input: preorder = [1,3]
Output: [1,null,3]
Constraints:
1 <= preorder.length <= 1001 <= preorder[i] <= 1000All the values of
preorderare unique.
Solution (Java)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int i = 0;
public TreeNode bstFromPreorder(int[] preorder) {
return bstFromPreorder(preorder, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
private TreeNode bstFromPreorder(int[] preorder, int bound) {
if (i == preorder.length || preorder[i] > bound) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[i++]);
root.left = bstFromPreorder(preorder, root.val);
root.right = bstFromPreorder(preorder, bound);
return root;
}
}
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).