Problem
A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible.
Design an algorithm to insert a new node to a complete binary tree keeping it complete after the insertion.
Implement the CBTInserter class:
CBTInserter(TreeNode root)Initializes the data structure with therootof the complete binary tree.int insert(int v)Inserts aTreeNodeinto the tree with valueNode.val == valso that the tree remains complete, and returns the value of the parent of the insertedTreeNode.TreeNode get_root()Returns the root node of the tree.
Example 1:
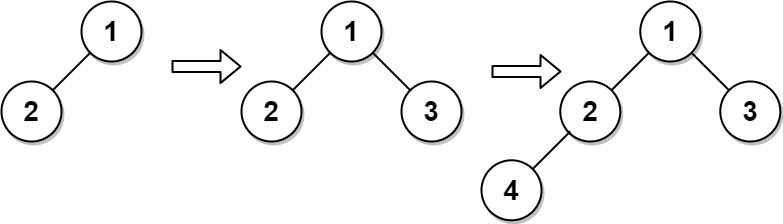
Input
["CBTInserter", "insert", "insert", "get_root"]
[[[1, 2]], [3], [4], []]
Output
[null, 1, 2, [1, 2, 3, 4]]
Explanation
CBTInserter cBTInserter = new CBTInserter([1, 2]);
cBTInserter.insert(3); // return 1
cBTInserter.insert(4); // return 2
cBTInserter.get_root(); // return [1, 2, 3, 4]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 1000].0 <= Node.val <= 5000rootis a complete binary tree.0 <= val <= 5000At most
10^4calls will be made toinsertandget_root.
Solution (Java)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class CBTInserter {
public CBTInserter(TreeNode root) {
tree.add(root);
for (int i = 0; i < tree.size(); ++i) {
TreeNode node = tree.get(i);
if (node.left != null)
tree.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
tree.add(node.right);
}
}
public int insert(int v) {
final int n = tree.size();
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(v);
TreeNode parent = tree.get((n - 1) / 2);
tree.add(node);
if (n % 2 == 1)
parent.left = node;
else
parent.right = node;
return parent.val;
}
public TreeNode get_root() {
return tree.get(0);
}
private List<TreeNode> tree = new ArrayList<>();
}
/**
* Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such:
* CBTInserter obj = new CBTInserter(root);
* int param_1 = obj.insert(val);
* TreeNode param_2 = obj.get_root();
*/
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).